
August 13, 2024
What is OWASP?
The Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP) is an international non-profit organization dedicated to the security of web applications. OWASP has no commercial intentions and is open to all people interested in the topic of data and operational security of web applications. They provide resources such as documentation, tools, videos, and forums. Their famous project is the OWASP Top 10.
What are the OWASP Top 10?
The OWASP Top 10 is a regularly updated report that describes security risks for web applications, focusing on the 10 most critical vulnerabilities. The list has been compiled by the eponymous OWASP non-profit organization since 2003 and is updated every two to three years. In 2021, the OWASP Top 10 list was updated to its latest version.
The OWASP TOP 10 - 2021
The current OWASP Top 10 from 2021 has three new categories compared to the previous version from 2017: Insecure Design, Software and Data Integrity Failures, and Server-Side Request Forgery. Additionally, some categories have been renamed or redefined.
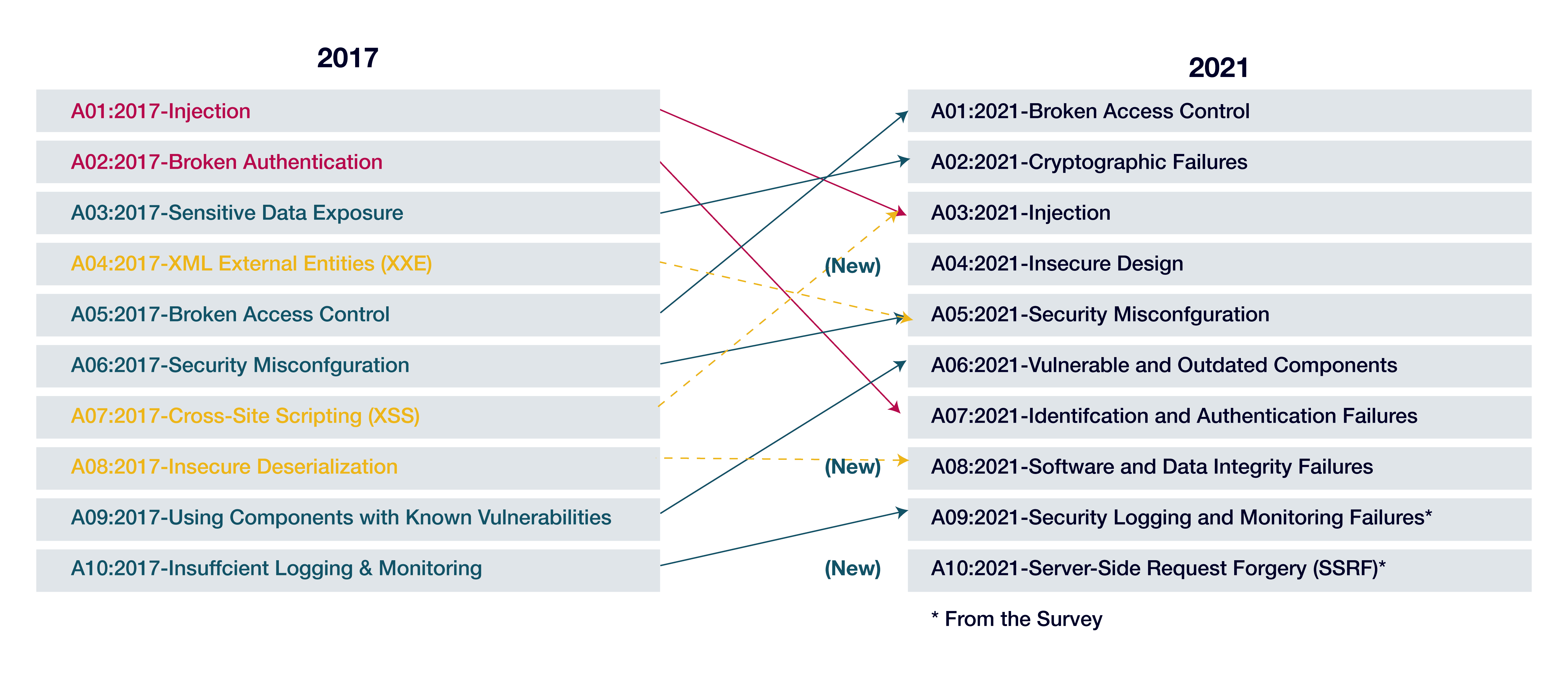
A01:2021 - Broken Access Control
Access Control focuses on implementing restrictions for authenticated users so that they cannot perform actions beyond their permission level. Flaws in access control can result in uncontrolled data leaks of sensitive information or allow manipulation of accessible data.
Real-Life Example
An inadequate access control allowed a security expert to access the CD keys for every game on Steam.
A02:2021 - Cryptographic Failures
Cryptographic failures refer to errors in the encryption of data and data transfers as well as the lack of adequate encryption methods. Deficiencies in cryptography clearly affect the security of applications and their data. Attackers can steal and alter data due to insufficient security, which can lead to serious repercussions. This was previously referred to as “Sensitive Data Exposure,” but this name is not entirely accurate as it describes more symptoms and effects than causes. The new name focuses on encryption errors, as previously indicated. The disclosure of sensitive data such as private keys or passwords often occurs when vulnerabilities arise.
Real-Life Example
As part of Google's Project Zero, a vulnerability was discovered in Cloudflare's edge servers that allowed the reading of memory potentially containing sensitive data, some of which was cached by search engines. This vulnerability was named Cloudbleed.
A03:2021 - Injection
Injection is a hacking technique used when user input is interpreted by an application. This can lead to the text being processed as a command or parameter. The processing depends “naturally” on the technology used.
For example, a malicious user can exploit parameters in a SQL query so that they can read, modify, or delete sensitive or even confidential data. This manipulation is called SQL Injection.
Another type of injection is Command Injection. This allows the attacker to start or stop system commands on the server, enabling them to gain control over the system.
An Injection Attack occurs when untrusted data is sent to a web application to a code interpreter through a form submission or other data transmission. Data or the entire application can be compromised by malicious code placed by an attacker.
A04:2021 - Insecure Design
Essentially, an Insecure Design means that no security controls are integrated into the application throughout the entire development cycle. This can have far-reaching and profound effects on security, as the application itself is not designed with security in mind.
Such negligence leads to the fundamental design and basis of the application being insecure, opening the door for a multitude of security gaps - ultimately leading to information disclosure or complete compromise of the application.
Insecure Design addresses vulnerabilities arising from known/unknown flaws in application/software architecture. This category focuses on risks resulting from errors in architectural and design drafts. As explained by OWASP, these differ from risks associated with implementation flaws. Even well-implemented insecure designs are vulnerable to attacks. Insecure software designs lack security controls and business risk profiling. This makes them highly susceptible to attacks.
A05:2021 - Security Misconfiguration
Security misconfigurations focus on security controls that are either insecure or improperly configured. This vulnerability is usually due to one of the following reasons:
Incorrectly configured systems such as firewalls, web servers, or web applications.
Allowing and installing unnecessary features, such as ports, services, pages, accounts, or permissions.
Default accounts/passwords are enabled or unchanged.
The software is not up to date.
Real-Life Example
Incorrectly configured HTTP headers on the website of the US Department of Defense. The X-XSS-Protection header was included, but set to DENY, which is intended for the X-Frame options. The expert therefore recommended changing this value to 1; mode=block. The original report can be viewed here.
A06:2021 - Vulnerable and Outdated Components
Modern web developers use frameworks and libraries in their web applications. These are software components that help developers avoid redundant work and provide the necessary functionality. Common examples are frontend frameworks like React and smaller libraries that add share icons or A/B testing. To orchestrate larger attacks, some attackers look for vulnerabilities in these components. Some of the most popular components are used in hundreds of thousands of websites. An attacker finding a vulnerability in one of these components could make hundreds of thousands of websites vulnerable.
Real-Life Example
On December 9, 2021, a vulnerability for Remote Code Execution (RCE) in the Apache logging package Log4j2, version 2.14.1 was reported.
The Log4j2 library is an open-source logging library provided by the Apache Software Foundation that is commonly used in online applications and services for logging development, operations, and security purposes.
A07:2021 - Identification and Authentication Failures
These security vulnerabilities in authentication and session management were previously referred to as Broken Authentication. Here, vulnerabilities associated with logins and authentications are listed. These include: insufficient protection against brute force, credential stuffing, credential cracking, storing passwords in plaintext, and lack of or insufficient multi-factor authentication. This category is still a staple of the Top 10, but with the increasing popularity of standardized development frameworks, this category is becoming rarer.
Real-Life Example
Uber failed to limit the https://biz.uber.com/confirm endpoint, which would allow an attacker to open business accounts using brute force and take rides on their behalf. This vulnerability was reported on HackerOne. The original report can be viewed here.
A08:2021 - Software and Data Integrity Failures
The new categories relate to vulnerabilities in software updates with unverified integrity of critical data and CI/CD pipelines. Such flaws can arise in applications using plug-ins, libraries, or modules from unverified and untrusted sources, repositories, or Content Delivery Networks (CDNs). An insecure CI/CD pipeline can provide cybercriminals access to inject malicious code and compromise systems. A similar source of error could be the automatic update feature of most applications, which does not necessarily include thorough integrity checks. This opens the door for attackers to spread updates aimed at creating vulnerabilities.
Real-Life Example
The most well-known example of a failing software and data integrity system is the SolarWinds Orion attack, which focused on compromised update mechanisms.
A09:2021 - Security Logging and Monitoring Failures
This category placed tenth in 2017 and has been expanded this year with additional types of vulnerabilities. In general, logging and monitoring are used to detect, escalate, and respond to proactive security breaches. Issues can arise, for example, when the fault generates no or only insufficient log entries, logs are maintained only locally, or thresholds for alert and escalation processes are not properly defined.
A10:2021 - Server-Side Request Forgery (SSRF)
Server-Side Request Forgery (SSRF) occurs when a web application cannot validate a user-specified URL when requesting a remote resource. In this way, an attacker can force an application to send a crafted request to an unexpected destination, even if it is protected by a firewall, VPN, or another type of network access control list (ACL). OWASP has noted that the severity of SSRF is increasing due to cloud services and complex architectures.



